

Moreover, students will get exposure to the practical use of modern technology. This will not only reduce time needed for data acquisition but will also increase precision and accuracy of the data. that if the general labs could be equipped with microprocessors and mobile data collection tools, the trend of working in lab will be directed more toward better data analyses instead of spending a lot of time in data collection. In a recent study, it is proposed by Chen et al.
MEASURING ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB MANUAL
Manual ways to record readings are being used which consume a lot of time and are less accurate. One important problem in School and High School labs (especially in developing countries) is unavailability of modern devices to acquire data.
MEASURING ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB SOFTWARE
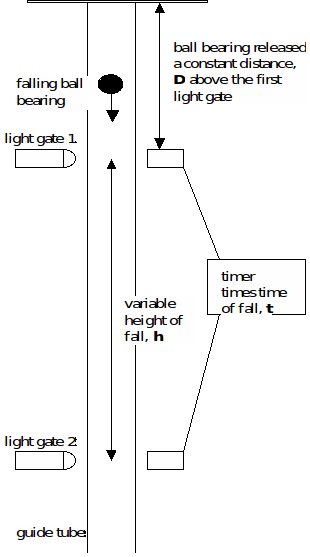
Hardware and software prepared for the experiment are sufficient to examine movement of ordinary objects during free fall, therefore the experiment can be easily settled in a laboratory for the purpose of learning and teaching. After repeated experiments, value of gravitational acceleration was found to be 9.805 m/s2. The shape of the distance-time graphs obtained from the experimental setup was in good agreement with the predicted graphs and the calculated values of g lie within the expected range. Acceleration during the free fall was then determined by applying the standard kinematic equations. Readings were taken at different intervals during the fall to obtain distance time curves. Experimental data on the free fall of a plastic box through the air was gathered with the help of an ultrasonic distance sensor (HC-SR04). In this study, a simple Arduino-based experiment was designed to examine the acceleration of the object during free fall and to calculate the value of “g” (acceleration due to gravity).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
